
Surgery is a specialized branch of medicine focused on the use of operative techniques to address a variety of medical conditions, including injuries, diseases, and deformities. The field encompasses a wide range of procedures, classified mainly as elective or emergency. Elective surgeries are planned in advance and are often performed for non-life-threatening conditions, while emergency surgeries are conducted in response to acute medical crises, necessitating immediate intervention to preserve life or function.
Surgical procedures can also be classified based on the patient’s care setting. Outpatient surgeries, usually performed in an ambulatory facility, allow patients to return home on the same day after the procedure. In contrast, inpatient surgeries require patients to stay in a hospital for recovery, as these procedures may involve more complex interventions that need extended monitoring and care. Each type of surgery plays a critical role in patient health management and the overall healthcare system.
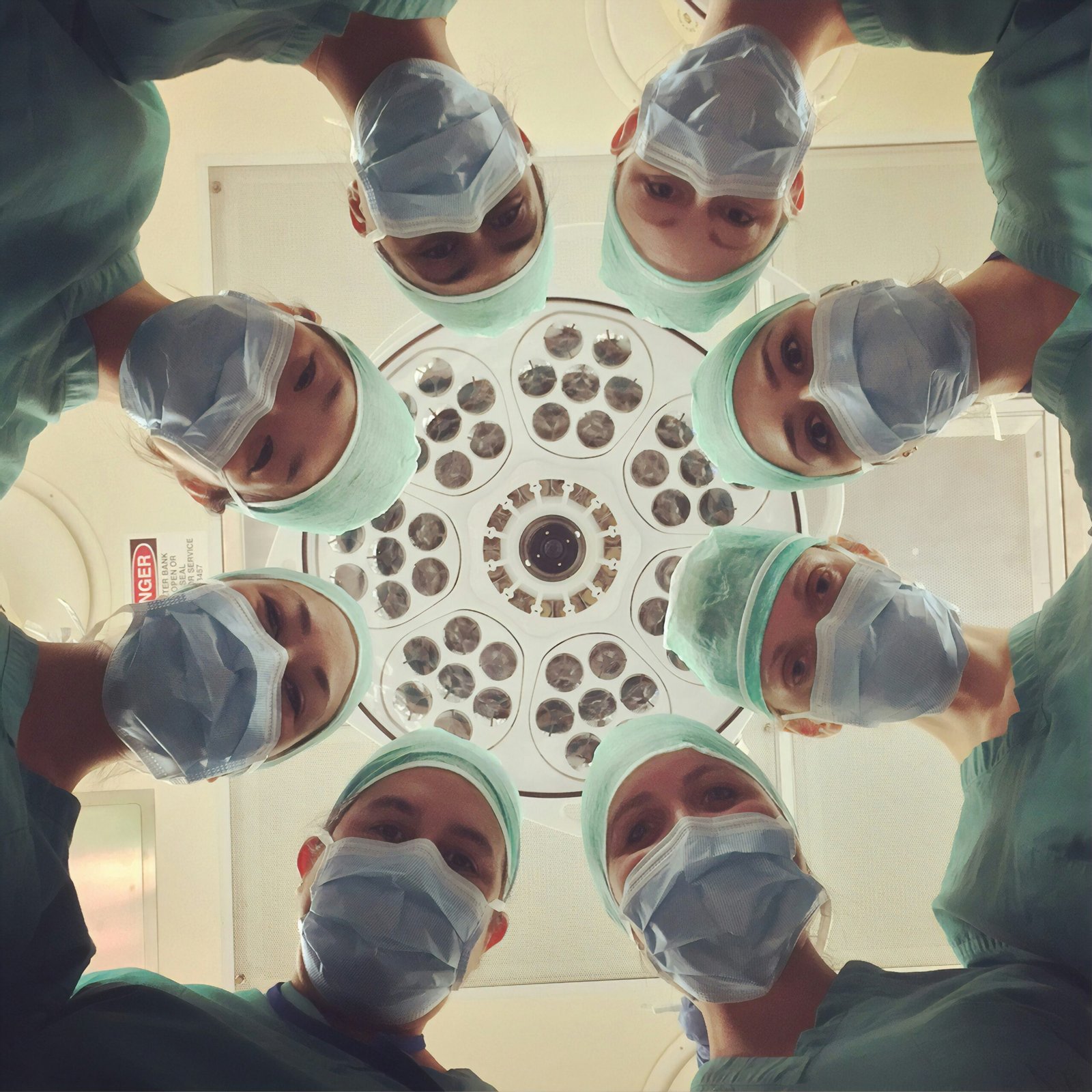
The successful execution of surgical procedures is heavily reliant on a dedicated surgical team comprising various professionals. Lead among these are surgeons, who are skilled practitioners responsible for performing the surgery itself. Accompanying them are anesthesiologists, who manage patient anesthesia and ensure comfort throughout the operation. Additionally, surgical nurses play a vital role in facilitating the procedure, managing instruments, and providing crucial support to both the surgeon and the patient. This collaborative effort among surgical staff is essential for achieving optimal surgical outcomes and minimizing potential risks associated with the operation.
Types of Surgical Procedures
Surgery is a field that encompasses a variety of procedures aimed at diagnosing, treating, or preventing medical conditions. Surgical procedures can be generally classified into two main categories: major surgeries and minor surgeries, each with distinct characteristics and applications. Major surgeries tend to involve significant bodily invasions, higher risks, and longer recovery times. Examples include open-heart surgery, complex tumor resections, and major joint replacements. These procedures typically require hospitalization and extensive post-operative care.
In contrast, minor surgeries are less invasive and often performed on an outpatient basis. They usually entail shorter recovery periods and lower risk profiles. Examples of minor surgical procedures include skin biopsies, arthroscopic surgeries, and the removal of small cysts. Despite being termed “minor,” these procedures still require precision and expertise to ensure optimal outcomes.
Further categorizing surgical procedures, we find open surgery, minimally invasive surgery, and robotic-assisted surgery. Open surgery involves larger incisions to allow direct access to the area of concern. While this traditional method can effectively address complex issues, it often results in longer recovery times and greater post-operative pain. In contrast, minimally invasive surgery utilizes smaller incisions, leading to reduced tissue damage, shorter hospital stays, and improved recovery trajectories. Techniques such as laparoscopy and endoscopy exemplify this category.
Robotic-assisted surgery is a modern advancement that incorporates robotic systems to enhance the surgeon’s abilities. This approach often results in increased precision and improved patient outcomes. Various specialties, including orthopedic and cardiovascular surgery, employ robotic technologies to refine complex procedures. Overall, understanding the different types of surgical interventions and their specific applications is crucial for patients and healthcare providers alike in making informed decisions regarding surgical care.
The Surgical Process: From Preparation to Recovery
The surgical process is a comprehensive journey that encompasses various stages, starting from the initial preparation to post-operative recovery. The first step in this journey involves pre-operative evaluations, where healthcare professionals assess the patient’s overall health to identify any potential risks associated with the surgery. This evaluation may include blood tests, imaging studies, and an assessment of the patient’s medical history. Patients are also required to provide informed consent, ensuring they understand the procedure and its implications.
Once the preparations are complete, the patient enters the surgical stage. On the day of the surgery, the patient is taken to the operating room, where anesthesia is administered. Anesthetics play a crucial role in ensuring that patients remain pain-free and unconscious during the surgical procedure. Depending on the nature of the surgery, the anesthesia may be local, regional, or general. With anesthesia in place, the surgeon begins the operation, which can range from minimally invasive techniques to more extensive procedures, depending on the medical necessity.
Following the surgical intervention, post-operative care becomes critical. Patients are typically monitored in a recovery area, where healthcare staff observe vital signs and manage any discomfort. Recovery time can vary considerably, influenced by factors such as the complexity of the procedure, the patient’s overall health, and adherence to post-operative instructions. It is essential for patients to receive clear guidance from their healthcare team regarding activity restrictions, wound care, and signs of potential complications.
In addition to immediate post-operative care, follow-up visits are integral to ensuring a smooth recovery. These appointments provide opportunities for healthcare professionals to monitor healing, address any concerns, and reinforce patient education regarding long-term care and lifestyle modifications. Overall, understanding the entire surgical process—from preparation to recovery—is imperative for patients as it fosters a sense of control and knowledge about their health journey.
Common Myths and Misconceptions about Surgery
Surgery, as a medical discipline, is often accompanied by numerous myths and misconceptions that can lead to unnecessary fear and anxiety amongst patients. One common belief is that all surgeries are highly dangerous and carry significant risks. While it is true that any surgical procedure comes with inherent risks, many surgeries are performed routinely and safely. In fact, advancements in surgical techniques and anesthesia have dramatically reduced the risks associated with many procedures, making them considerably safer than in previous decades.
Another misconception is that surgeons perform surgeries without sufficiently considering alternative treatment options. In reality, ethical medical practice emphasizes a thorough evaluation of all possible treatment pathways. Healthcare providers typically discuss non-surgical options first, and surgery is recommended only when it is deemed the most effective solution for a patient’s specific condition. This process ensures that patients are fully informed and involved in their own care decisions.
Patients may also believe that surgeries always result in long recovery times and significant pain. While some surgical procedures may require extensive recovery periods, many minimally invasive techniques now offer quicker recovery times, allowing patients to return to their normal activities sooner than anticipated. Moreover, modern pain management strategies are continually evolving, enabling a more comfortable recovery experience.
Furthermore, there is a prevalent idea that surgery is a last resort and should be avoided until all other treatments fail. While it is important to explore all options, some conditions necessitate surgical intervention, and delaying necessary procedures can sometimes lead to complications or worsening health statuses. Ultimately, it is crucial for patients to engage in open dialogues with their healthcare providers, ensuring that they understand both the realities and the rationale behind surgical interventions, thereby dispelling these misconceptions.
Hi, this is a comment.
To get started with moderating, editing, and deleting comments, please visit the Comments screen in the dashboard.
Commenter avatars come from Gravatar.